Obstetrician &
Gynaecologist


Adolescent gynecological care focuses on the reproductive health of young girls, typically between 10 and 16 years old. It involves preventative care, addressing common concerns like menstrual irregularities, and providing education on reproductive health. Routine check-ups, often recommended between 13 and 15, are crucial for establishing a relationship with a gynecologist and familiarizing young people with their bodies, says Rainbow Hospitals.




Obstetrics care, also known as OB care, focuses on the medical care of women during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, ensuring the health of both the mother and the baby. This specialty is a subfield of obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) and is concerned with managing pregnancy, labor, delivery, and the immediate postpartum period.


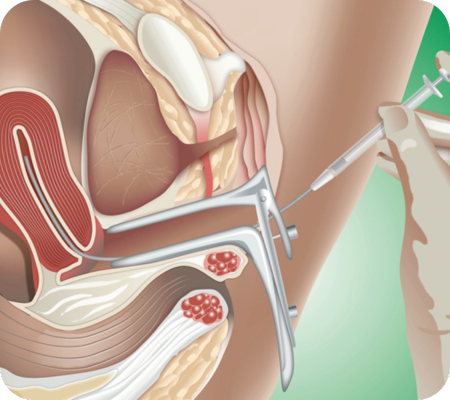
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a fertility treatment where sperm is placed directly into the uterus, increasing the chances of fertilization. It's a less invasive procedure than in vitro fertilization (IVF) and can be a viable option for couples with certain types of infertility, such as unexplained infertility, male factor infertility, or cervical issues.


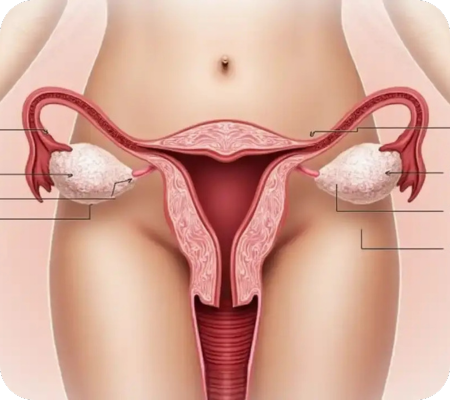
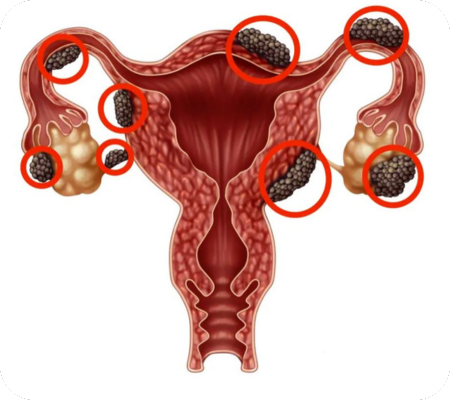
PCOD care involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and sometimes medication to manage symptoms and improve overall health. Focusing on weight management, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, along with addressing insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances, are crucial for managing PCOD.


Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) starts to grow outside the uterus—such as on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or pelvic lining. Even though it’s outside the uterus, this tissue acts like normal endometrial tissue: it thickens, breaks down, and bleeds every month during your period. But since it has no way to exit the body, it causes pain, inflammation, and scar tissue (adhesions).


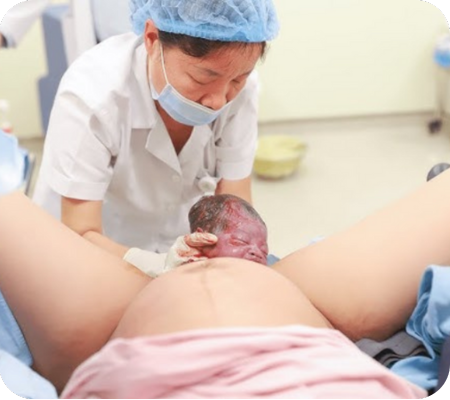
Normal Delivery, also known as Vaginal Delivery, is the natural way of giving birth, where the baby is delivered through the birth canal (vagina) without the need for major surgery. It is the most common and safest method of childbirth for women with low-risk pregnancies.


A Caesarean Delivery, commonly known as a C-section, is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby through incisions in the mother's abdomen and uterus. It is performed when a vaginal delivery is not safe for the mother or baby, or when certain complications arise during pregnancy or labor.


Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) refers to any bleeding from the uterus that deviates from a normal menstrual cycle in terms of regularity, frequency, volume, or duration. This can include bleeding between periods, excessively heavy bleeding, or bleeding after menopause. Essentially, it's any uterine bleeding that isn't considered typical for a woman's menstrual cycle.


A High-Risk Pregnancy is one in which the health of the mother, baby, or both is at greater risk than usual. This can be due to existing health conditions, complications that develop during pregnancy, or special circumstances like multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.). It means that extra care, monitoring, and medical attention are needed to ensure a safe pregnancy and delivery.



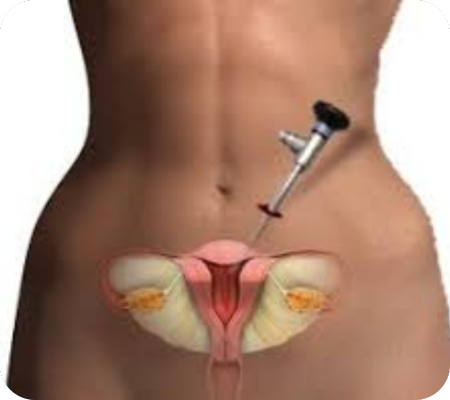
Gynecological laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to examine or operate on the female pelvic organs—such as the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and surrounding tissues—using a thin, lighted tube called a laparoscope. This technique is done through small incisions in the abdomen, so it involves less pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.


Menstrual disorders are any deviations from a woman's normal menstrual cycle, encompassing various issues like heavy bleeding, painful periods, or absent periods. These disorders can affect the regularity, duration, and intensity of a woman's menstrual cycle. They can be caused by hormonal imbalances, structural issues in the reproductive organs, or even psychological factors.


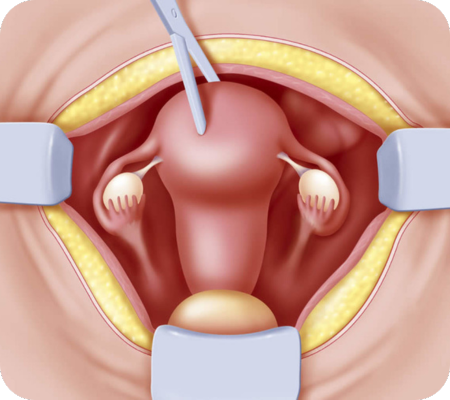
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure where a woman's uterus (womb) is removed. This can be done for various reasons, including medical conditions affecting the uterus or the desire to cease menstruation and ability to become pregnant. The procedure can involve removing the entire uterus (total hysterectomy) or just part of it (partial or supracervical hysterectomy). Other organs like the cervix, ovaries, or fallopian tubes may also be removed during the procedure, depending on the specific reason and the surgeon's recommendations.